Charles Babbage

Charles Babbage, (born December 26, 1791, London, England—died
October 18, 1871, London), English mathematician and inventor
who is credited with having conceived the first automatic
digital computer.
The idea of mechanically calculating mathematical tables first
came to Babbage in 1812 or 1813. Later he made a small
calculator that could perform certain mathematical computations
to eight decimals. Then in 1823 he obtained government support
for the design of a projected machine, the Difference Engine,
with a 20-decimal capacity. Its construction required the
development of mechanical engineering techniques, to which
Babbage of necessity devoted himself. In the meantime (1828–39),
he served as Lucasian Professor of Mathematics at the University
of Cambridge.
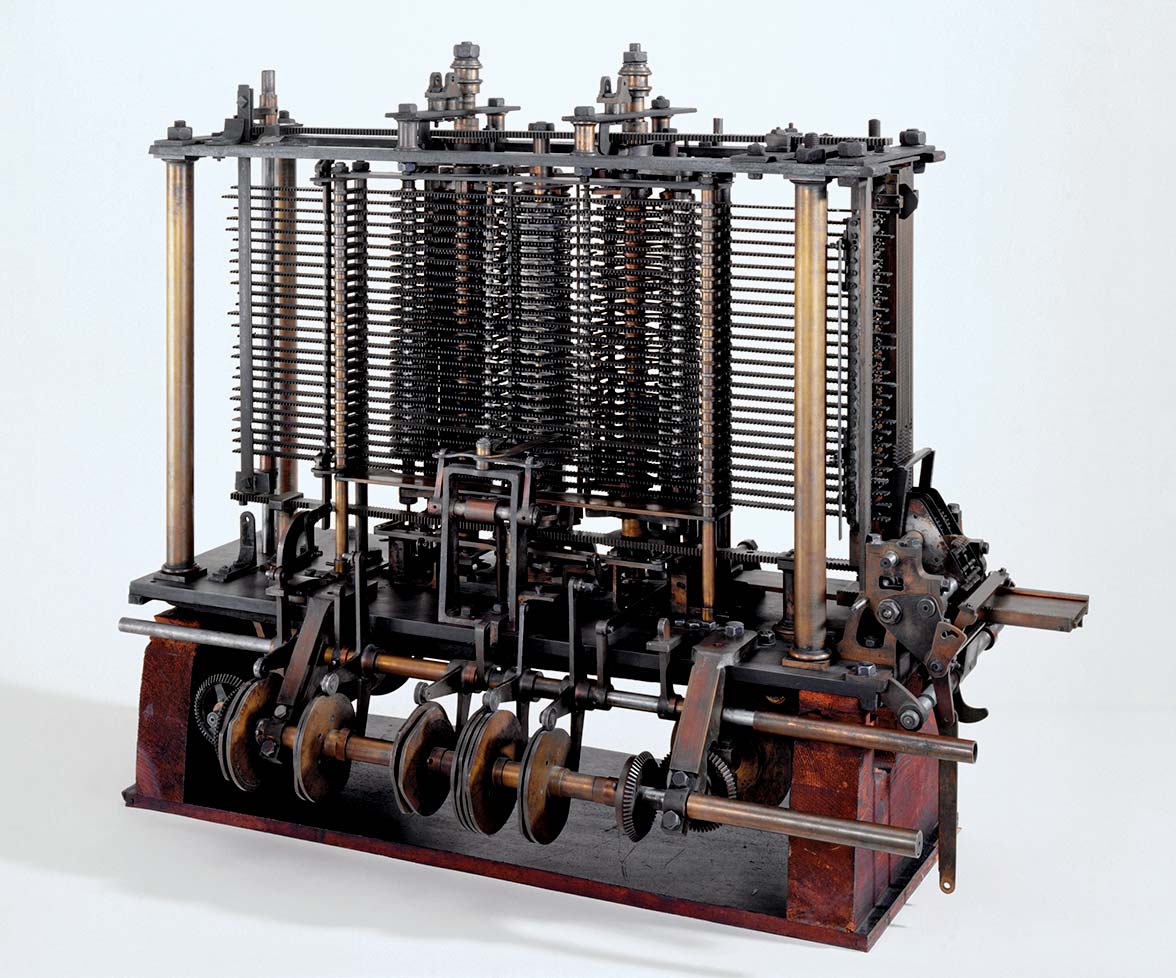
During the mid-1830s Babbage developed plans for the Analytical
Engine, the forerunner of the modern digital computer. In that
device he envisioned the capability of performing any
arithmetical operation on the basis of instructions from punched
cards, a memory unit in which to store numbers, sequential
control, and most of the other basic elements of the present-day
computer.
In 1843 Babbage’s friend mathematician Ada Lovelace translated a
French paper about the Analytical Engine and, in her own
annotations, published how it could perform a sequence of
calculations, the first computer program. The Analytical Engine,
however, was never completed. Babbage’s design was forgotten
until his unpublished notebooks were discovered in 1937. Babbage
lived and worked for over 40 years at 1 Dorset Street,
Marylebone, where he died, at the age of 79, on 18 October 1871;
he was buried in London's Kensal Green Cemetery. According to
Horsley, Babbage died "of renal inadequacy, secondary to
cystitis.